Infinity Bank Memorandum
TO: DATE:
FROM: ITEM NO:
SUBJECT: ANALYSIS OF THE KEY FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS FOR INFINITY BANK
ISSUE:
The Infinity Bank is facing challenges due to major structural and managerial changes in the banking sector. The bank is taking steps to boost its customer and product profitability through various studies, such as, the product profitability analysis and customer profitability analysis (CPA). We need to evaluate and understand the main cause of our failures and come-up with effective solutions that will drive the success of the bank.
Recommendations
- This study recommends that Infinity Bank managers should reject the proposed supermarket strategy and implement the CPA findings to help the firm gain a competitive edge. On the other hand, the product profitability analysis provides numerous benefits for the success of Infinity Bank, but it should not be considered into its long-term reform plan. Cross holding consumers are presented to be more profitable, and thus, Infinity Bank managers should create an incentive system encouraging consumers to buy multiple products.
- Consequently, the managers should provide incentive promotional offers that aim to upgrade the "CA only" consumers to the other 3 consumer segments by centralizing operational services and transferring specific transactional charges to the consumers. They should also adjust the bank's policies to lower credit and raise interest rates for credit card and mortgage default consumers.
- Finally, the bank should consider upgrading its systems to fit the current operational status of banks and effectively compete with other commercial banking institutions. Therefore, it should prioritize on restructuring its managerial and operational activities by incorporating the current trend of increasing the number of phone support systems, utilizing an effective online banking system and centralized operations, and lowering physical branches.
Background
The bank was controlling more than 1,800 retail branches in the U.K., being among the largest banks. As per our management, branch networks were key to Infinity bank's banking strategy, though this turned out to be less cost-effective. According to analysts, the bank was unable to cope with the numerous structural changes such as bank alternatives, deregulations, and new technological innovations that altered the interaction means between customers and banks.
Infinity bank’s retail division viewed branches as shop and by 2003, our branch managers did not realize the most profitable products and customers, and thus, did not optimize sales. The branch managers were responsible for the branch’s P&L, and they were supposed to make money and profits by selling products. This did not turn well as many managers argued that customers can be profitable overall, despite buying unprofitable products. And thus, the proposed retail divisions was rejected as too complicated since the predictability of a product sale leading to a better relationship or future sale of a profitable product could not be guaranteed.
By 2003, we hired Philippa Smith, who believed that the firm's product-profitability study was critical in detecting variations in customer profitability in each product and even at the consumer relationship level. She sampled 1000 customers per product cross-holding from the bank's databases and utilized the initial product profitability study to link the bank's services and costs of services to individual consumers. From her analysis, the most profitable consumer holdings were those that comprised various products and also maintained huge balances.
The Product Profitability Analysis, headed by our Senior Operations Manager, Karine Cheneviere revealed the following conclusions and surprises.
- The study noted the difficulty in attributing costs to activities.
- According to the study, management overheads and fixed costs (in brand management, technology, and capital management) were significant and had no relation to the products.
- It further concluded that the most profitable products were multiple products.
The study revealed two surprising revelations, which were;
- The current accounts, which are a critical banking product was more unprofitable and;
- Mortgages were extremely profitable.
Banking institutions currently experience the challenge of measuring the profitability of their offerings since the existing reporting structures are majorly designed for purposes such as R&D, supporting cost center cost budgets, and optimizing taxation treatments. This makes the cost allocation models overly complex and not reflecting the institutions value chain resource consumption.
Banks in many cases have all the information necessary to manage and undertake Product Profitability Analysis, but the available information is always scattered in many source systems. Furthermore, the availability of no typical rules to regulate the management of these resources and the lack of proper methodologies, structures, and the analytics to combine the resources for computation adds-up to the inability of banking institutions to undertake the product profitability analysis. Generally, many banking institutions cannot account for the cost of the products and the services they are offering.
The solution to this challenge relies on employing a disciplined and systematic approach, where data is entangled, cleaned, and then aggregated to allow for the allocation of costs against costs elements and the assigning of cost elements in the value chain (Menicucci and Guido, 96). Consequently, effective rules and regulation are utilized to roll up costs across the value chain steps and transparently distribute them to products. This creates a wellspring of data that is necessary in a banking institution’s proper decision-making.
| CA Only | CC only | M Only | |
| Revenue | 425 | 654 | 355 |
| Associated Costs | 889 | 271 | 97 |
| Profits | -463 | 383 | 258 |
Table 1: Profit margins for Infinity Bank's three main products for the year 2003
The Infinity bank is considering phasing out their most unprofitable product, current accounts. This is based on the product profitability analysis undertaken and its profit/loss performance from the year 1999 to 2003 (Exhibit 3). As observable from the table above, current accounts made 463 million loss in 2003 while the other two main products, credit card and mortgage made profits of 383 and 258 respectively. Coupled with the utilization of the supermarket strategy, it is imperative from this statistics to consider phasing out the current accounts. The supermarket strategy demands that branch managers maximize sales and profits by selling only the profitable products.
The supermarket strategy in the banking sector gives consumers with an easy, one stop access to financial products and the capability of undertaking various financial activities in one integrated channel. Despite this, it only allows the Infinity bank branch managers to focus on the most profitable products. These among other factors are key to our consideration to phase-out the current accounts. Provided below are the advantages and the disadvantages of the supermarket strategy as it is applied in Infinity Bank.
Advantages
The Infinity bank adopted the “Supermarket Strategy” due to the following advantage;
- It emphasized on each branch focusing on its profitability, and thus, decentralizing the firm's profitability to help maximize profits.
Disadvantages
- The supermarket strategy builds a lot of pressure to branch managers and staff.
- It does not offer for the evaluation of the long-term strategic objectives of a branch or the entire entity.
- It exclusively focuses on quantitative profit drivers.
On the other hand, if the bank utilizes the consumer individual profitability analysis approach, then current accounts should not be phased out. This profitability analysis approach assesses customer profitability and maximizes value from the most profitable consumers. Based on the approach, current accounts are of significance to the bank as they help increase the total profits achieved by the bank via the revenues generated by consumers with cross-holdings. As such, phasing out current accounts will most probably affect the cross-holding accounts' profitability and, thereby, affecting the probable total profits of the bank. In this case, despite their unprofitability, current accounts are an important product in the success of the bank as they boost the cross-holding profits. Therefore, the bank will not be phasing out the current accounts but will devise means through which to maximize their profitability.
All the other considerations aside, Infinity Bank can ensure current accounts are more profitable by utilizing the following possibilities.
- The bank can share some of the current account service costs with the customers. These can include the introduction of transaction charges and account service charges.
- It can also implement the cross-selling strategy where the current accounts can be of importance in building relationships with other bank services and products.
- Consequently, it can implement the need-based segmentation, where it would design products based on consumer needs.
- Utilizing the integrated liquidity management as well as implementing lean processes between back and front office.
- Engaging with the customer in their financial journey. This can be offering advices to clients on the items like saving plans, and acquiring effective mortgaging. This will boost customer trust and improve their reliance to the bank.
The bank further performed the Customer Profitability Analysis (CPA) in its attempts to ensure profits. According to Ilhan, Tanis, and Kosan (610), customer profitability analysis is the process by which revenue and costs are allocated to the customers, either through individual customer accounts or customer segments to allow for the computation of the profits achieved by the individual customer accounts or segments. At infinity bank, the customer profitability analysis was of significance in assessing the potentials of the supermarket strategy. Consequently, it was utilized as an improvement measure for the profitability study conducted by Karine. Philippa Smith believed that the product profitability study was critical in identifying the consumer variations, and therefore, she used the consumer profitability analysis to identify the variations that are critical in examining consumer profitability.
In general, firms utilize CPA studies as an important tool in making critical marketing decisions (Helgesen, 251). Furthermore, through the study, it can be used by firms to offer insights on risks associated with its strategic positioning and costs, thereby, indicating areas that require service improvement. Consumer profitability analysis is a regular exercise performed by banking institutions. Generally, it should be a live system in the bank management to allow for continuous effective decision-making. As such, branch managers at Infinity bank should constantly be applying the analytic technique to improve their critical decision-making. It is important based on the following;
- It notes the cost transparency where it is highly possible to identify the reasons why a cost is traced to a product, a transaction, and to a customer.
- It helps analyze and improve the process efficiency leading to the cost efficiency improvement. This will allow the branch managers to understand resource usage and production.
- Importantly, it also allows managers to understand the costs and the costs components linked to a product.
- Lastly, it is an important method of knowing what consumers largely purchase and the revenue generated from the purchases. Hence, allowing for early detection in the customers’ buying behavior.
Furthermore, CPA is of high significance to the product profitability study. The product profitability study mainly focuses on examining product variations in relation to profits while the customer profitability study examines customer variations in relation to profits. As such, the consumer profitability study will link customers to products. Consequently, it identifies and explains the profitability difference of customers as well as customer behavior across various cross-holdings. To improve the pilot study by Philippa Smith, the firm should;
- Use a much bigger sample size
- Incorporate the competitors' consumer bases
- Utilize the prospective customer profitability analysis, where the future costs of service and revenues are analyzed and predicted.
The Philippa Smith’s CPA highlighted various key variation and conclusions
Conclusions
- Single product consumers are least profitable than multiple product consumers.
- The CC + M account consumers with huge balances are more profitable.
- There exist distinct profitability variations between consumers in every product, even for those with similar account balances. According to the Philippa study, huge account balances produce higher rates of interest at a constant set-up cost and service level.
Variations
The sources of variation in Philippa Smith's study arose from the difference between cost drivers and revenues. For instance, Smith noted that there was unprofitability among many multiple account customers. She also noted that customers with high balance mortgages yielded higher profits. Therefore, mortgages had a positive effect on customer profits as those lacking it provided a net loss to the company. The second variation in the customer profitability study was the differing risk of default that the customers who held the mortgages were exposed to. Consequently, another variability depicted by Smith's study is that the profitability of credit card and current account products largely depended on customer behavior
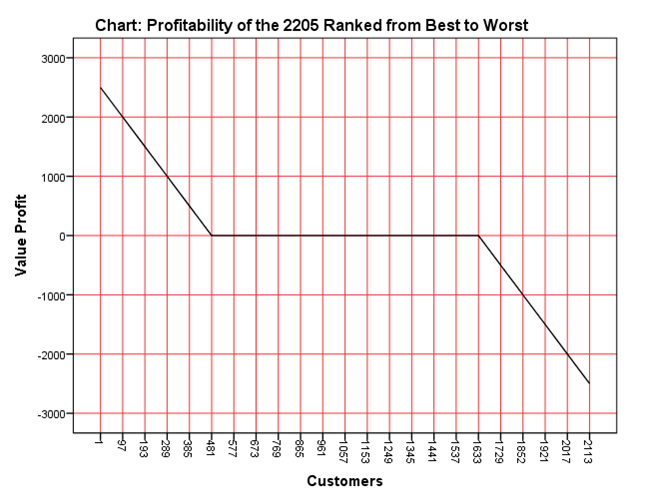
Figure 1: Profitability of the 2205 Customers (Best to worst)
From Smith's study findings, there is a significant variation of profitability in every product line as well as for consumers with a similar balance in the same product line. Based on this evaluation, the supermarket strategy does not make sense since consumer profitability is merely informative as there are differences in product profitability in a particular product line. Multiple product customers are depicted to be more profitable, and thus, utilizing the supermarket strategy will discourage sales of unprofitable products. As earlier indicated in this paper, some of the unprofitable products like current accounts are an important asset in customer profitability via the cross-holdings. Despite being unprofitable, current account consumers are important profit-making products as they purchase mortgages and credit cards. Furthermore, implementing the supermarket strategy together with the customer profitability analysis is useful to the bank as it allows Infinity Bank to effectively maximize profits through consumers and products. On the other hand, implementing the supermarket strategy will not be cost-friendly for Infinity Bank.
Generally, the traditional cost accounting techniques do not help identify costs related to customers and products and the delivery and distribution costs that pertain to individual consumers (Larry and Skousen, 115). CPA helps determine consumer activities and track the costs that are linked to specific consumers. This is an important asset for management as it offers unique customer managerial insights that include;
- Protection for the more profitable consumers.
- Negotiating for mutual win relationships that are aimed at reducing costs for specific consumers.
- Providing the necessary information that helps in discounting to achieve business with a lower cost of serving consumers.
- CPA is also important in capturing profitable customers from competitors. By understanding the profitability of a specific segment of customers in relation to products, firms can easily understand and lure customers from competitors.
- As well as restructuring a firm's pricing plan, for instance, it can be used to restructure the pricing of expensive products and services on the basis of the service costs.
As for the case of the Infinity Bank, the firm can;
- Provide promotional offers to current account customers to encourage them to shift to cross-holding product lines.
- Upgrade the existing current account products.
- Consequently, it can raise the interest rate credit card limits for credit card default consumers.
It is with great pleasure that I send this letter on behalf of myself and the Infinity Bank, presenting the key financial solutions that have impacted the bank in the recent times and the best strategies to counter them and resolve the challenges. It is our aim that the recommendations in this letter will lead to a successful business venture and the growth of Infinity Bank.
It is time Infinity Bank gained its early banking fame and prowess. We should seize the existing opportunities and maximize on the analytical processes to assess our profitability and performance. Above all, we should ensure to add more consumers to our current list as this is the first step to ensuring successful banking.
Prepared by
Signature:
Name:
Work Cited
Dalci, Ilhan, Veyis Tanis, and Levent Kosan. "Customer profitability analysis with time-driven activity-based costing: a case study in a hotel." International Journal of contemporary hospitality Management 22.5 (2010): 609-637.
Helgesen, Oyvind. "Are loyal customers profitable? Customer satisfaction, the customer (action) loyalty and customer profitability at the individual level." Journal of Marketing Management 22.3-4 (2006): 245-266.
Menicucci, Elisa, and Guido Paolucci. "The determinants of bank profitability: empirical evidence from European banking sector." Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting 14.1 (2016): 86-115.
Walther, Larry M., and Christopher J. Skousen. Managerial and Cost Accounting Exercises III. Bookboon, 2017: 1-130

