Solved: H82PEP – Process Engineering Project
C2-C4 separator
TASK 1 - Mass and energy balance
Students are required to complete a mass and energy balance for the C2-C4 process in order to gain familiarity with the process, and understand the interconnectivity between the different operations. This will form a key part of your ability to understand and undertake Tasks 3 and 4 later on in the module. Each student has different data to work with, so do not over-rely on comparisons with the results of your peers.
Your task is to complete the mass and energy balance to include all process material flows, heating and coolant flows, and some temperatures. In some cases this will require assumptions to be made on your part. You should study the accompanying P&ID and process description document carefully, as this is key to completing the mass and energy balance. A separate excel file containing your individual data can be viewed on Moodle.
Submission
You should fill in the template using excel and submit electronically via Moodle as an excel file. It will be marked using an algorithm, so do not include any formulae within the spreadsheet, and do not change the formatting.
The final submission deadline for Task 1 is 16:00 on Friday 24th February.
In addition, students will be permitted to submit once, prior to 16:00 on 17th February, and will receive a formative score and indication correct/incorrect values within the completed template.
The mark for Task 1 will count towards 20% of the mark for this module.
Accompanying documents:
Appendix 1 – Process description
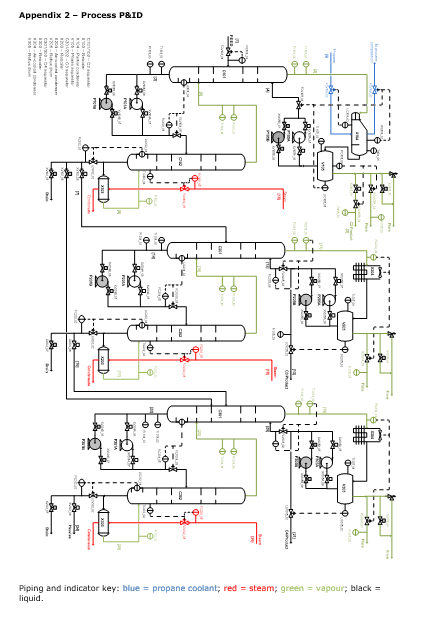
Appendix 2 – Process P&ID
Appendix 3 – Mass and Energy Balance Template
Appendix 4 – Physical Properties
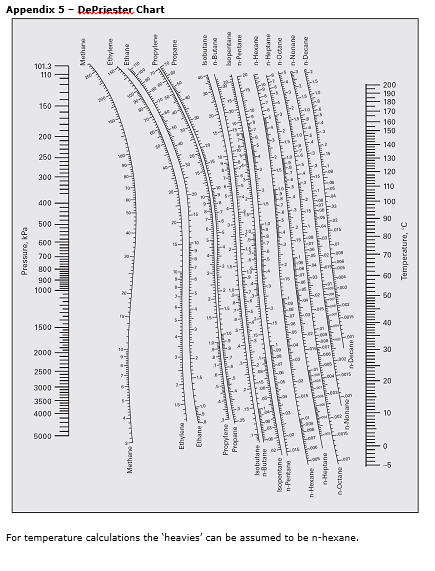
Appendix 5 – DePriester Chart
Appendix 1 – Process Description
The process separates gaseous components as part of a wider LNG manufacturing operation. This plant has four product streams; C2, C3, C4 and ‘heavies’. The four products are produced from six interconnected distillation columns. The columns operate in pairs, with one condenser and reboiler per two columns. The pressure is reduced between each pair of distillation columns, and pressure provides the driving force to transport the process fluids between each column set.
Unit Operations
A complete P&ID is shown in Appendix 2, with the major unit operations indicated in the table below.
| Code | Description | Function/Specification |
| C101 | C2 rectifying column | C4 and above negligible in vapour leaving C1 and below negligible in liquid leaving |
| C102 | C2 stripping column | Reduce C2 levels in liquid leaving to target C4 and above negligible in vapour leaving |
| X103 | Reboiler | Vaporise part of liquid leaving C102. Steam is used as the heating medium. |
| X104 | Condenser | Condense part of the vapour leaving C101. The temperature is determined by the boiling point of propane, which in turn is controlled by the shell-side pressure. |
| V105 | Phase separator | C1 and below negligible in liquid leaving. Also acts as a reflux drum, with buffer storage capacity. |
| C201 | C3 rectifying column | C5 and above negligible in vapour leaving C2 and below negligible in liquid leaving |
| C202 | C3 stripping column | Reduce C3 levels in liquid leaving to target C5 and above negligible in vapour leaving |
| X203 | Reboiler | Vaporise part of liquid leaving C202. Steam is used as the heating medium. |
| X204 | Air-cooled condenser | Condense vapour leaving C201. Fan speed can be varied to adjust the temperature and pressure. |
| V205 | Reflux drum | Provide buffer capacity and pressure relief |
| C301 | C4 rectifying column | Negligible heavies in vapour leaving C3 and below negligible in liquid leaving |
| C302 | C4 stripping column | Reduce C4 levels in liquid leaving to target Heavies negligible in vapour leaving |
| X303 | Reboiler | Vaporise part of liquid leaving C302. Steam is used as the heating medium. |
| X304 | Air-cooled condenser | Condense vapour leaving C301. Fan speed can be varied to adjust the temperature and pressure. |
| V305 | Reflux drum | Provide buffer capacity and pressure relief |
- The Feed enters C101 close to saturation, but slightly sub-cooled
- Vapour leaves the reboilers X103, X104 and X105 at saturation
- Steam enters X103, X104 and X105 at saturation, and leaves as a saturated liquid
- Liquid leaves V105, V205 and V305 in a sub-cooled state

Appendix 4 – Physical Properties
| Substance | Molar latent heat of vaporisation (kJ/kmol) |
| ethane | 11879 |
| propane | 24787 |
| i-butane | 27500 |
| n-butane | 28684 |
| i-pentane | 32600 |
| n-pentane | 33968 |
| heavies | 50000 |
| water | 44733 |
Latent heats can be assumed to be accurate and independent of temperature over the ranges utilised in the C2-C4 separation process.