Essentials of Healthcare Finance
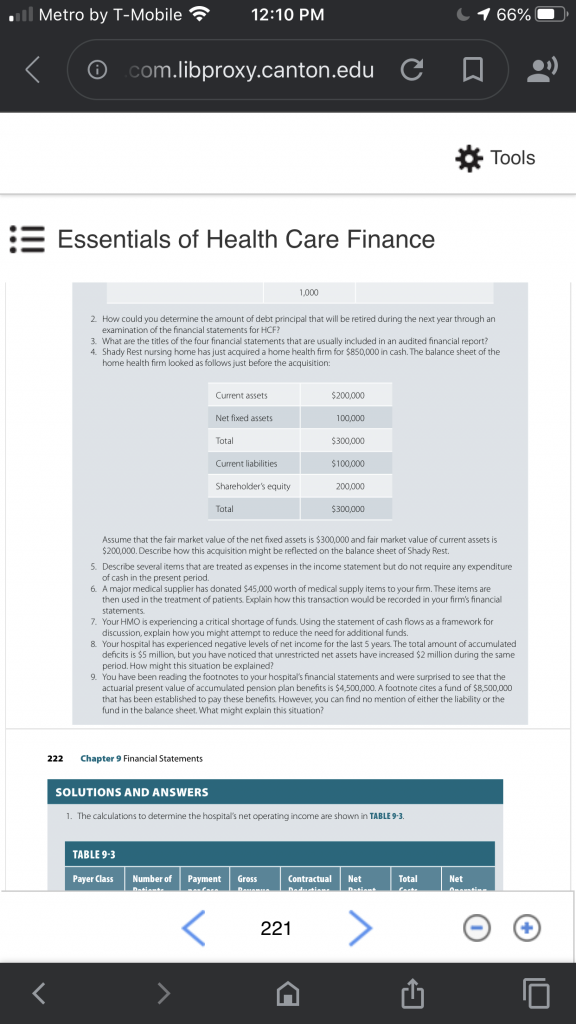
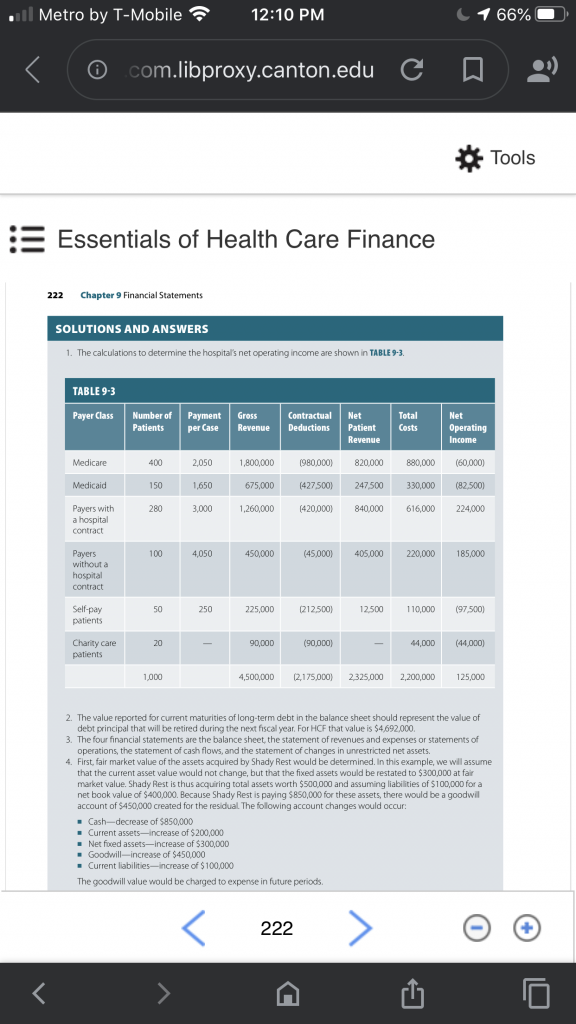
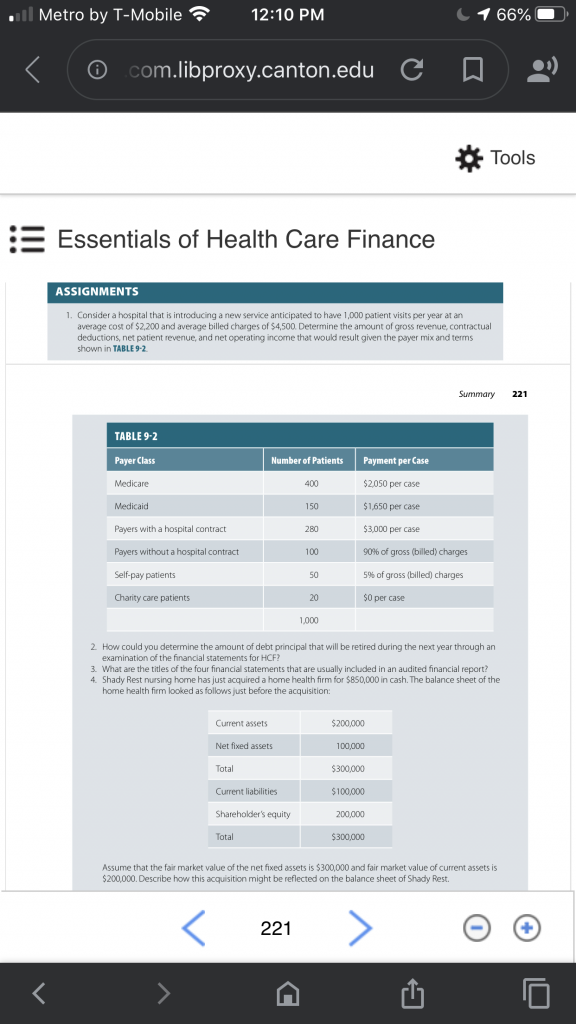
Consider a hospital that is introducing a new service anticipated to have the following data: 1,070 patient visits per year $2,200 average cost per visit $4,500 average billed charges (gross revenue) per visit. Determine the amount of gross revenue, contractual deductions, net patient revenue, total costs, and net operating income that would result given the following payer volume and payment terms.
To get you started, I developed the chart below. Please complete the chart and show ALL of your work / mathematical formulas to receive credit. There is a bonus question (5 points)
- What is the hospitals operating margin for this new service?
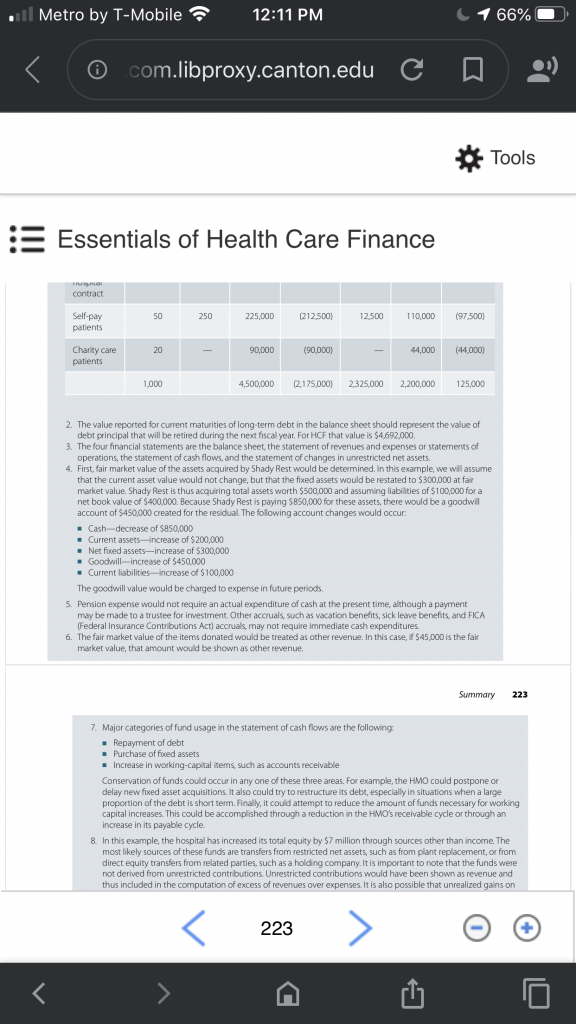
Payers with a hospital contract 320 $3,000 Payers without a hospital contract 120 90% of gross (billed) charges Self-Pay Patients 50 5% of gross (billed) charges Charity Care Patients 20 0 Total 1,070 Expense and expenditure may not be equivalent in any given period. Statement of cash flows is a statement that reports inflows and outflows of cash during the accounting period in the categories of operations, investing, and financing.
The heading of every financial statement should contain the name, title, specific date of statement, and unit of measurement. The Balanced Scorecard is an attempt to enhance the value of information and to exploit the capability of information technology to deliver true value to decision-makers. Balanced Scorecards simply state that reporting should be available on those key attributes that really affect performance. More data is of little value if it does not provide information to a decision-maker that can be used to improve the performance of the firm.
The Balanced Scorecard allows managers to look at the business from four important perspectives: Customer Internal business process Innovation and learning Financial "Dashboard" reporting is a natural subset of Balanced Scorecards and is being increasingly used in almost all sectors of the economy to keep managers focused on critical areas that will affect overall firm performance. The following are the four key elements of dashboard reporting: What is most important to the firm s success? What are the critical drivers that influence performance attainment? What are the most relevant measures that reflect critical driver relationships? What relevant benchmarking data is available to assess performance? Ratio analysis is a common approach for detailed analysis of the financial statements of healthcare organizations. Ratio analysis asks the question: "What is the ratio of one line item to another?" For instance, a question might be: "How many dollars are there in current assets as compared to current liabilities?" As opposed to being limited to just one financial statement at a time, ratios may combine items from several different financial statements.
� Traditionally there are four general categories of ratios: Liquidity, Profitability, Activity, and Capital structure. Liquidity ratios answer the question: "How well is an organization positioned to meet its short-term obligations?" Profitability ratios answer the question (as one might expect): "How profitable is an organization?" Activity ratios answer the question: "How efficiently is an organization using its assets to produce revenues?" Capital structure ratios answer two questions: 1) "How are an organization s assets financed?;" and 2) "How able is this organization to take on new debt?" Once calculated, the ratios can be compared to some meaningful standard, such as goals, standards, historical levels, and industry levels. Such comparisons yield clues as to how well an entity is functioning and how it might improve its operational performance and financial position.
Ratio analysis formulas: Return on equity = net income / equity or net assets Total asset turnover = revenue / assets Operating margin = operating income / total net revenue Days in Accounts Receivables = net patient receivables/ (Net patient service revenue /365) Long term to debt asset ratio = notes payable / unrestricted net assets Age of plant = less accumulated depreciation / depreciation Fixed asset turnover ration = total revenue / net property and equipment Days cash on hand = (cash and cash equivalents /(total expense -depreciation)/365) Managed-care, health maintenance organizations (HMOs), preferred provider organizations (PPOs), physician organizations (POs), physician hospital organizations (PHOs), capitation, medical service organizations (MSOs), consumer-directed health plans (CDHP), and integrated delivery systems (IDSs) are all terms and acronyms that are used freely in today s health care arena. These terms often represent different things to different people and often change in meaning over time.
One common thread runs through all of these terms: the issue of change and market reform that is sweeping the health care industry. The planning/control cycle has four major components: Strategic planning, planning, implementing and controlling. The purpose of strategic planning is to identify the organization s mission and strategy in order to position the organization for the future. A major activity of the strategic planning process is an assessment of the organization s external and internal environments. Whereas the organization s strategic planning process has a long-term focus, it also develops shorter term tactical and operational plans which are more specific and identify short-term goals and objectives in more detail in regard to marketing/production, control, and financing the organization.Consider a hospital that is introducing a new service anticipated to have the following data: 1,070 patient visits per year $2,200 average cost per visit $4,500 average billed charges (gross revenue) per visit Determine the amount of gross revenue, contractual deductions, net patient revenue, total costs, and net operating income that would result given the following payer volume and payment terms. To get you started, I developed the chart below.
Please complete the chart and show ALL of your work / mathematical formulas to receive credit. There is a bonus question (5 points) - What is the hospitals operating margin for this new service? Hospital Payer Class Data Payer Class Number of Patient Visits Payment per Visit Total gross patient revenue Contractual Deductions Total Net Patient Revenue Total Costs Net Operating Income Medicare 355 $2,050 Medicaid 205 $1,650 Payers with a hospital contract 320 $3,000 Payers without a hospital contract 120 90% of gross (billed) charges Self-Pay Patients 50 5% of gross (billed) charges Charity Care Patients 20 0 Total 1,070 Expense and expenditure may not be equivalent in any given period. Statement of cash flows is a statement that reports inflows and outflows of cash during the accounting period in the categories of operations, investing, and financing. The heading of every financial statement should contain the name, title, specific date of statement, and unit of measurement. The Balanced Scorecard is an attempt to enhance the value of information and to exploit the capability of information technology to deliver true value to decision-makers.
Balanced Scorecards simply state that reporting should be available on those key attributes that really affect performance. More data is of little value if it does not provide information to a decision-maker that can be used to improve the performance of the firm. The Balanced Scorecard allows managers to look at the business from four important perspectives: Customer Internal business process Innovation and learning Financial � �Dashboard� reporting is a natural subset of Balanced Scorecards and is being increasingly used in almost all sectors of the economy to keep managers focused on critical areas that will affect overall firm performance. The following are the four key elements of dashboard reporting: What is most important to the firm�s success? What are the critical drivers that influence performance attainment? What are the most relevant measures that reflect critical driver relationships? What relevant benchmarking data is available to assess performance? � Ratio analysis is a common approach for detailed analysis of the financial statements of healthcare organizations. Ratio analysis asks the question: �What is the ratio of one line item to another?� For instance, a question might be: �How many dollars are there in current assets as compared to current liabilities?� As opposed to being limited to just one financial statement at a time, ratios may combine items from several different financial statements.
� Traditionally there are four general categories of ratios: Liquidity, Profitability, Activity, and Capital structure. Liquidity ratios answer the question: �How well is an organization positioned to meet its short-term obligations?� Profitability ratios answer the question (as one might expect): �How profitable is an organization?� Activity ratios answer the question: �How efficiently is an organization using its assets to produce revenues?� Capital structure ratios answer two questions: 1) �How are an organization�s assets financed?;� and 2) �How able is this organization to take on new debt?� Once calculated, the ratios can be compared to some meaningful standard, such as goals, standards, historical levels, and industry levels. Such comparisons yield clues as to how well an entity is functioning and how it might improve its operational performance and financial position. Ratio analysis formulas: Return on equity = net income / equity or net assets Total asset turnover = revenue / assets Operating margin = operating income / total net revenue Days in Accounts Receivables = net patient receivables/ (Net patient service revenue /365) Long term to debt asset ratio = notes payable / unrestricted net assets Age of plant = less accumulated depreciation / depreciation Fixed asset turnover ration = total revenue / net property and equipment Days cash on hand = (cash and cash equivalents /(total expense -depreciation)/365) Managed-care, health maintenance organizations (HMOs), preferred provider organizations (PPOs), physician organizations (POs), physician hospital organizations (PHOs), capitation, medical service organizations (MSOs), consumer-directed health plans (CDHP), and integrated delivery systems (IDSs) are all terms and acronyms that are used freely in today�s health care arena. These terms often represent different things to different people and often change in meaning over time. One common thread runs through all of these terms: the issue of change and market reform that is sweeping the health care industry. The planning/control cycle has four major components: Strategic planning, planning, implementing and controlling.
The purpose of strategic planning is to identify the organization�s mission and strategy in order to position the organization for the future. A major activity of the strategic planning process is an assessment of the organization�s external and internal environments. Whereas the organization�s strategic planning process has a long-term focus, it also develops shorter term tactical and operational plans which are more specific and identify short-term goals and objectives in more detail in regard to marketing/production, control, and financing the organization.